Java Constructors
Hello there! If you’re here, you’re probably looking to understand Java constructors. Well, you’re in the right place! Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Java Constructors
A constructor in Java is a special method that is used to initialize objects. The constructor is called when an object of a class is created. It can be used to set initial values for object attributes.
public class Main {
int x; // Create a class attribute
// Create a class constructor for the Main class
public Main() {
x = 5; // Set the initial value for the class attribute x
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main myObj = new Main(); // Create an object of class Main (This will call the constructor)
System.out.println(myObj.x); // Print the value of x
}
}The output of the above code will be 5.
Detailed Explanation
In this code snippet, we’re creating a class called Main with one attribute x. The constructor for this class is defined with public Main(). Inside the constructor, we’re setting the value of x to 5. When we create a new object of the class Main in the main method, this constructor is called, and x is initialized to 5.
Explanation with Diagram
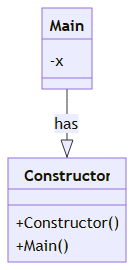
Main class that has a ConstructorThe diagram shows a Main class that has a Constructor. The Constructor is a default constructor (with no parameters). The Main class has an attribute x that can be initialized by the Constructor.
Constructor Parameters
Constructors can also take parameters, which is used to initialize attributes. Let’s see an example:
public class Main {
int x;
public Main(int y) {
x = y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main myObj = new Main(5);
System.out.println(myObj.x);
}
}The output of the above code will be 5.
Detailed Explanation
In this example, we’re creating a class Main with one attribute x. The constructor for this class is defined with public Main(int y). Inside the constructor, we’re setting the value of x to y. When we create a new object of the class Main in the main method with a parameter 5, this constructor is called, and x is initialized to 5.
Multiple Parameters in Constructors
You can have as many parameters as you want. Let’s see an example:
public class Main {
int modelYear;
String modelName;
public Main(int year, String name) {
modelYear = year;
modelName = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main myCar = new Main(1969, "Mustang");
System.out.println(myCar.modelYear + " " + myCar.modelName);
}
}The output of the above code will be 1969 Mustang.
Detailed Explanation
In this example, we’re creating a class Main with two attributes modelYear and modelName. The constructor for this class is defined with public Main(int year, String name). Inside the constructor, we’re setting the value of modelYear to year and modelName to name. When we create a new object of the class Main in the main method with parameters 1969 and "Mustang", this constructor is called, and modelYear and modelName are initialized to 1969 and "Mustang" respectively.
Code Examples
Let’s take a look at two different complete codes with explanations and outputs.
Code Example 1
public class Rectangle {
int width;
int height;
// Constructor with parameters
public Rectangle(int w, int h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle myRectangle = new Rectangle(5, 10);
System.out.println("Width: " + myRectangle.width);
System.out.println("Height: " + myRectangle.height);
}
}In the above code, we have a Rectangle class with a constructor that takes two parameters: width and height. In the main method, we create a new Rectangle object with width 5 and height 10.
Detailed Explanation of Example 1
In this example, we’re creating a class Rectangle with two attributes width and height. The constructor for this class is defined with public Rectangle(int w, int h). Inside the constructor, we’re setting the value of width to w and height to h. When we create a new object of the class Rectangle in the main method with parameters 5 and 10, this constructor is called, and width and height are initialized to 5 and 10 respectively.
Code Example 2
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
// Constructor with parameters
public Student(String n, int a) {
name = n;
age = a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student myStudent = new Student("John", 20);
System.out.println("Name: " + myStudent.name);
System.out.println("Age: " + myStudent.age);
}
}In the above code, we have a Student class with a constructor that takes two parameters: name and age. In the main method, we create a new Student object with name John and age 20.
Detailed Explanation of Example 2
In this example, we’re creating a class Student with two attributes name and age. The constructor for this class is defined with public Student(String n, int a). Inside the constructor, we’re setting the value of name to n and age to a. When we create a new object of the class Student in the main method with parameters "John" and 20, this constructor is called, and name and age are initialized to "John" and 20 respectively.
Wrapping Up
Constructors in Java are a fundamental concept that every Java programmer should understand. They allow us to initialize our objects with specific values right when they’re created.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a constructor in Java?
A constructor in Java is a special method that is used to initialize objects. The constructor is called when an object of a class is created.
How is a constructor used in Java?
A constructor is used in Java to set initial values for object attributes. It’s called when an object of a class is created using the
newkeyword.Can a constructor have parameters in Java?
Yes, a constructor can have parameters in Java. These parameters are used to initialize the attributes of an object.
Can a constructor return a value in Java?
No, a constructor cannot return a value in Java. It does not have a return type and its name is the same as the class name.
Can we have multiple constructors in a Java class?
Yes, we can have multiple constructors in a Java class. This is known as constructor overloading.
What is a parameterized constructor in Java?
A parameterized constructor is a constructor that takes at least one parameter. This constructor is used to assign user-desired values to the instance variables of different objects.
What is a default constructor in Java?
A default constructor in Java is a constructor with no parameters. If you don’t define a constructor in your class, Java creates one for you, known as the default constructor.
Can we call a constructor directly in Java?
No, we cannot call a constructor directly in Java. It’s automatically called when an instance of the class is created.
Can a constructor be private in Java?
Yes, a constructor can be private in Java. This is used in singleton design patterns where you want to restrict the instantiation of the class to one object.
What is the difference between a constructor and a method in Java?
A constructor is a special method used to initialize objects in Java, whereas a regular method performs a function and can return a value. Constructors cannot return values and their name is the same as the class name, while methods can have any name and do not necessarily match the class name.
I hope these answers help clarify your understanding of Java constructors! If you have any more questions, feel free to ask. Happy learning!
Related Tutorials
- Java Methods
- Java Classes and Objects
- Java Inheritance
- Java Encapsulation
- Java Polymorphism
That’s all, folks! I hope you found this tutorial helpful. Happy coding!
Dr. Mehedi Hasan is a seasoned semiconductor professional, academic and web-designer with over a decade of experience in digital system design and verification as well as web development. Currently a Senior Engineer at AMD in Markham, Ontario, he plays a key role in the development and verification of cutting-edge chip technologies, earning multiple Spotlight Awards for his contributions.
Dr. Hasan holds a Ph.D. in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Saskatchewan and has served in both academia and industry across Canada, Bangladesh, Malaysia, and Saudi Arabia. His expertise spans web-development, UVM-based SystemVerilog verification, static timing analysis (STA), RTL design, and scripting in multiple languages including Python, TCL, Shell as well as web-development tools including HTML, CSS, Javascript.
Passionate about knowledge sharing and education, Dr. Hasan has also worked as an Assistant Professor in Ontario, Canada (at Lakehead University) and Bangladesh University. He is committed to building accessible learning environments and is the founder of SkillSeminary, a platform focused on simplifying complex tech concepts for learners worldwide.
When he's not immersed in chip verification or educational projects, Dr. Hasan enjoys mentoring, researching system development, and promoting open tech education.

